Ref. Demosthenes Papameletiou, Alexandre Zenié (Joint Research Centre), Dieter Schwela (World Health Organization),
and
Wolfgang Bäumler (University of Regensburg)
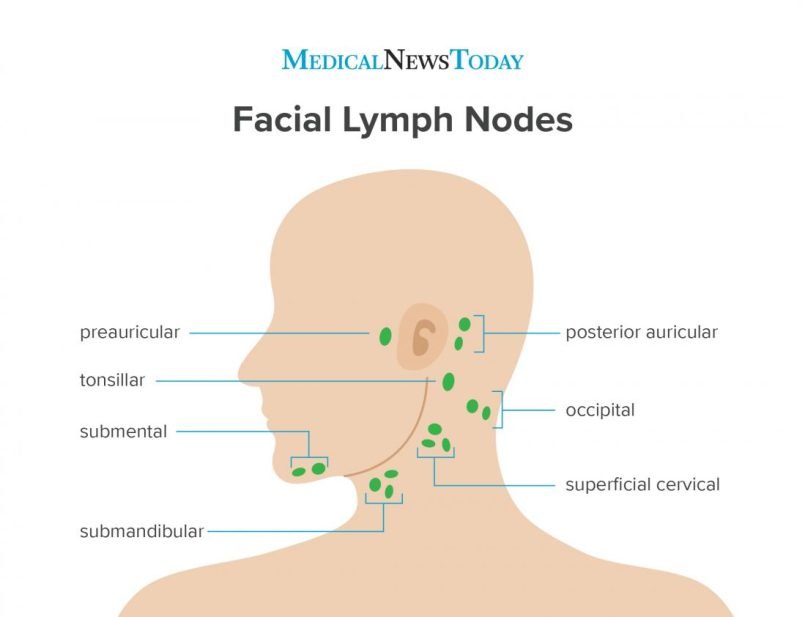
Using any kind of lasers break inks molecules in the skin, and push small particles ink via blood system to lymph nodes, make them swollen over time. Laser on Cosmetic tattoos liberates those small ink particles to all facial lymph nodes. And the same for the body tattoos. We have over 15 lymph nodes in the human body.
Better never use the laser on face tattoos (v scalp and cosmetic tattoos) tattoos. The risks of scaring and swollen lymph nodes are quite high.
I recommend using lasers tattoo removal only for the body tattoos and be aware of just limit it to a few sessions (2 or 3) to break down tattoo inks in smaller particles, then use expelling noninvasive and nonacidic technique as Magnetic tattoo removal.
Risks of the laser treatment of tattoos
Ref. Demosthenes Papameletiou, Alexandre Zenié (Joint Research Centre), Dieter Schwela (World Health Organization),
and
Wolfgang Bäumler (University of Regensburg)
On the other hand, the pigments remaining in the skin may exhibit different chemical characteristics as compared to non-irradiated pigments. Thus, there might be again a reaction of the immune system. Moreover, it was shown that carcinogenic amines are generated by a laser-induced cleavage of azo dyes74.

Allergy
Ref. Demosthenes Papameletiou, Alexandre Zenié (Joint Research Centre), Dieter Schwela (World Health Organization),
and
Wolfgang Bäumler (University of Regensburg)
As described above, laser treatment induces old/new chemical compounds in the skin, leading to allergic reactions.
A) Cinnabar (mercuric sulphide) is the most common cause of allergic reactions in tattoos and is probably related to a cell-mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction.
Others
Ref. Demosthenes Papameletiou, Alexandre Zenié (Joint Research Centre), Dieter Schwela (World Health Organization),
and
Wolfgang Bäumler (University of Regensburg)
According to a recent study in the USA77, computer simulations carried out in this study suggest that the breakup of tattoo particles is photoacoustic.
Cavitation bubbles can damage tissue surrounding the tattoo particles.



Tattoo Colorants in Skin
Ref. Wolfgang Bäumler
Department of Dermatology, University of Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany
The concentrations of tattoo ink in the skin depended on the size of the pigment crystals, the concentration of pigment applied to the skin surface, the desired colour strength of the tattoo, and the tattooing procedure using needles of different sizes and shapes. The mean value was estimated to be about 2.5 mg/cm2.
For more information Click On the button to download the PDF




